What is VMS?
Valiano Management System is the latest prepress automation management system released by Fujifilm, Japan. It is a server software built under Windows NT and specifically manages the drive space and SQL database. Data formats including pages, pictures, text, fonts, PDF files and even sound effects, such as file name, file type, file size, file location, related production software, production date, placement date, modification date, etc., can be stored in the database. In other words, the file itself is not stored in the database. This database only provides information for accessing the file. With this database, the management of files, the arrangement of work, and even the evaluation of costs can all be effectively controlled.
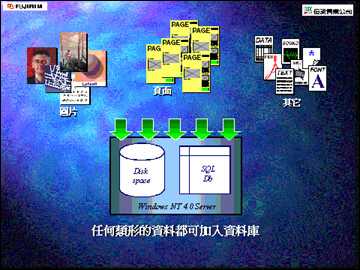
File input

The input files are sorted and processed by the VMS system:
â— The image file will be processed by the built-in high and low OPI system.
â— Various files will be stored in different types and categories.
â— At the same time, thumbnails for browsing can be created.
Everything is fully automated, and system administrators can set all their own steps and processes.

2. File processing and access

The file is stored in a separate folder categorized by each job:
â— The system will create a folder for each output job
â— Each job is accompanied by a unique code
â— When the file is placed, it will be categorized according to the operator's decision and automatically sorted
â—As required, the file will enter the OPI, and then generate a thumbnail for browsing
â— All file information, job data, and file processing data in this folder will be stored
3. File output

The SQL database in VMS records 4 different types of data:
â— File raw data - input the original data of the file, such as file name, file location, width, height, file size, etc.
â— File processing data - records of all related files processed, such as who has accessed the file, how it was processed on that machine, how long it was processed, and so on.
â— Workflow - Location of work in the entire process, those steps have been completed, work priorities and deadlines.
â— Work report records - data sent back from other devices, such as web output machines, all data is organized and stored with work.
4. Workflow data management

Once the data is established, it can be used to generate a complete and detailed report of any part of the entire workflow:
â— Tracking file usage records, confirming that the problem file and that part of the file use a lot of extra processing.
â— Track the workflow to find where the bottleneck is? Which job is the most efficient? Which workflows need improvement?
â— Analyze the time spent at each point in the file processing, color correction synthesis, turning fat side or output over the net, etc., to make a more accurate valuation, profit calculation.
â— The open database structure ensures that it can be combined with other database systems, financial systems and management systems.
5. System Management 
System managers can have complete control:
â— Work schedule management: Determine the processing procedure for each job in the process. You can set the order, use images, use names, and so on.
â— Operator authority: Different settings can be made for different operators to restrict different operators from having different file usage rights.
â— File Sorting: According to the characteristics and types of each file, different classifications can be assigned and sorted.
â— Remote control management: With the remote Java terminal, you can manage the data to sort or report, or even change the processing status, change the picture or icon.
