Principle of EMSA gel migration experiment
EMSA gel migration (Electrophoretic mobility shift assay)
Experimental principle
Gel migration or electrophoretic mobility experiment (EMSA) is a technique to study the interaction between DNA binding proteins and their associated DNA binding sequences, and can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis. This technique was originally used to study DNA binding proteins, and has been used to study the interaction of RNA binding proteins with specific RNA sequences.
Usually, the purified protein and crude cell extract are incubated with 32P isotope-labeled DNA or RNA probe, and the complex and unbound probe are separated on non-denatured polypropylene gel electrophoresis. DNA-complexes or RNA-complexes move slower than unbound probes. Isotope-labeled probes may be double-stranded or single-stranded depending on the binding protein studied. When detecting DNA binding proteins such as transcriptional regulators, purified proteins, partially purified proteins, or nuclear cell extracts can be used. When detecting RNA-binding proteins, depending on the position of the RNA-binding protein of interest, purified or partially purified proteins can be used, as can nuclear or cytoplasmic cell extracts. In competition experiments, DNA or RNA fragments and oligonucleotide fragments (specific) containing protein binding sequences and other non-related fragments (non-specific) are used to determine the specificity of DNA or RNA binding proteins. In the presence of competitive specific and non-specific fragments, specific binding is determined according to the characteristics and strength of the complex.
Experimental reagent
Important reagents:
Boitin-N4-CTP (invitrogen # 15918-18)
TdT (NEB # M0252L)
Poly (dI.dC) (sigma # P4929)
Hybond-N nylon membrane (Amersham # RPN303B)
Luminous substrate (Ningbo Weiao)
Buffer:
Buffer A (store at 4 ℃)
Hepes (pH7.9) 10mM
KCl 10mM
EDTA 0.1mM
DTT (fresh added) 1mM
PMSF (fresh added) 0.5mM
Buffer B (store at 4 ℃)
0.5M EDTA in PBS (pH7.4)
Buffer C (store at 4 ℃)
Hepes (pH7.9) 20mM
NaCl 0.4M
EDTA 1mM
DTT (fresh added) 1mM
PMSF (fresh added) 1mM
Buffer I (store at RT)
Tris (pH7.5) 0.1M
NaCl 1M
MgCl2 2mM
Buffer II (pH7.5) (store at RT)
Maleic acid 100mM
NaCl 150mM
Buffer III (store at RT)
Tris (pH9.5) 100mM
NaCl 100mM
MgCl2 50mM
Blocking Buffer (store at 4 ℃)
0.3% Tween-20, 0.3% Triton X-100, 5% BSA in Buffer I
Wash Buffer
0.3% Tween-20 in Buffer II
20 × SSC (1L pH7.0)
NaCl 175.3g
Sodium citrate 88.2g
10 × Binding Buffer (store at -20 ℃) ​​[Buy at the company (Biyuntian): 5 × binding buffer, containing Poly (dI.dC)]
Tris (pH7.5) 0.1M
KCl 0.5M
DTT 10Mm
Poly (dI.dC) (store at -20 ℃)
1mg / ml in TE (pH7.5)
SA-HRP (storage fluid store at -20 ℃ working fluid store at 4 ℃)
1mg / ml in 50% PBS (pH7.2) 50% Glycerin
5 × TBE (5L)
EDTA 18.612g
Boric acid 139.1175g
Tris 272.565g
5 × TdT Reaction Buffer (store at -20 ℃) ​​(pH7.2)
Sodium cacodylate 0.5M
CoCl2 10mM
TCEP 1mM
Biotin-N4-CTP (store at -20 ℃)
Biotin-N4-CTP 50mM
Tris (pH7.5) 10mM
EDTA 1mM
Experimental procedure
Biotinylated probe:
1. Add the reactants in the following order, mix gently, do not vortex
Ultra-pure water 25μl
5 × TdT Reaction Buffer 10μl
Probe (1μM) 5μl
Biotin-N4-CTP 5μl
TdT (2U / μl) 5μl
30 minutes at 37 ℃
2. Add 2.5μl 0.2M EDTA to stop the reaction;
3. Add 50μl of phenol: chloroform, vortex briefly, centrifuge at 15000g for 2min, keep the upper aqueous phase, and store at -20 ℃;
4. Mix the two labeled primers in equal volume before combining the reaction, anneal the primers at 90 ° C, and naturally cool to 4 ° C until use.
Extract nucleoprotein:
1. 2 ~ 3 × 106 density lay 60mm cell culture plate, culture for about 12h;
2. Remove the cell culture medium and wash the cells once with PBS;
3. Add 1mL Buffer B to the culture plate, scrape the cells and collect in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube;
4. Centrifuge at 1000g for 2min, and aspirate the supernatant;
5. Add 160μl Buffer A, resuspend the pellet and incubate on ice for 20min;
6. Add Buffer A containing 2.5% NP-40, vortex for 10s, centrifuge at 15000g at 4 ℃ for 5min;
7. Aspirate the supernatant, add 40μl Buffer C, vortex at 4 ℃ for 25min, centrifuge at 18000g at 4 ℃ for 5min;
8. Pipette 2μl supernatant to measure protein concentration by Bradford method, and store the rest at -80 ℃
Configure non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel (take 6% concentration as an example)
5 × TBE 1mL
30% Ac-Bi 2mL
40% Glycerin (glycerin) 625 μL
DDW (double distilled water) 6.125mL
10% AP 150μL
10% TEMED 100μL
Use 0.5 × TBE pre-cooled at 4 ° C as the electrophoresis buffer, pre-electrophoresis at 100V for 30-60min (time is indefinite, run to two thirds of the whole gel)
EMSA (refer to PIERCE kit)
1. Proof of specificity
The probe sequence used for the first time needs to prove whether it specifically binds to the target protein and determine the position of the target band.
According to the system in "Steps", do the following four parallel combination experiments:
(On the basis of adding ddw, 10 × binding buffer, Poly (dI.dC))
1) Biotin-labeled probe
2) crude protein extract
3) Crude protein extract + 200-fold concentration of non-labeled probe (ie cold probe)
4) Crude protein extract + 200-fold concentration of unlabeled mutation probe (probes with multiple mutation types can be designed to see if they can compete for binding)
5) Protein crude extract + antibody
React for 10 min at room temperature, then add biotin-labeled probe;
Continue the reaction at room temperature for 20 minutes and do EMSA detection.
Results analysis, if the following experimental results appear
1) Display free probe position
2) Display free probe position and migration band position
3) Only free belt, no migration belt
4) Same as 2) Band type
It proves that the probe specifically binds to the target protein.
step:
1. Add the reactants in the following order, mix gently (20μl system)
ddw ——
10 × binding buffer 2μl
Poly (dI.dC) 1μl (The above text has been stated by the company)
Nucleoprotein crude extract 4-10μg (mildly mixed)
Biotin labeled probe 0.5μl
Incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes, add 4 μl of 6 × Loading Buffer (TAKARA), load 10-20 μl, and run at 100V to bromophenol blue at two thirds.
2. Soak the nylon membrane in 0.5 × TBE for at least 10min before turning
The pre-cooled 0.5 × TBE was used as the transfer buffer 100V to transfer the glue on the nylon membrane for 45min.
3. Under the UV BOX, face the UV light source with the side close to the film, and cross-link for 15 min with 254 nm excitation light (UV cross-linker 1200 energy, 2 shots)
4. Add 25mL Blocking Buffer, block at about 70rpm for 30min on a decolorizing shaker
5. Dilute SA-HRP in 12mL Blocking Buffer 1 with decolorizing shaker at 70rpm for 20min
(The film washing process is all performed on the decolorizing shaker, about 100-140prm)
6. Buffer II 25ml, 5min
7. wash buffer 25ml 15min
8. Buffer III 25ml 5min × 2 times
9. 0.1% SDS in 2 × SSC, 5min × 2 times
10. 0.1% SDS in 1 × SSC, 10min × 2 times
11. 0.1% SDS in 0.5 × SSC, 5min × 2 times
12. Slightly dry the membrane on the filter paper, add it to the luminescent reaction solution (Ningbo Aowei) diluted 1:20, and act for 1-5 minutes. Seal the nylon membrane in the plastic wrap (to avoid wrinkles and bubbles) , 1-5min dark room exposure, detection signal.
Precautions
Use this protocol rendering
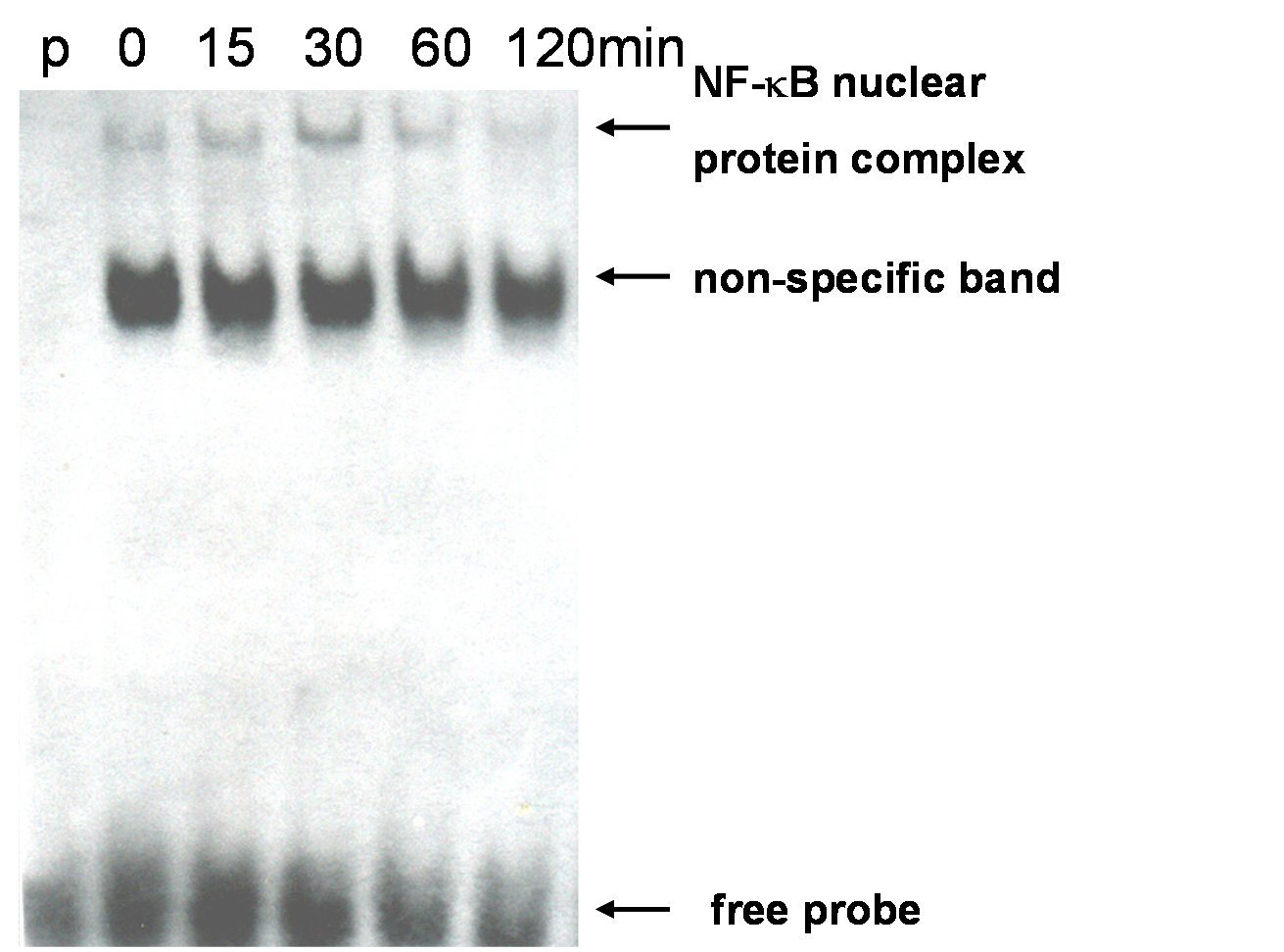
Figure 1. MELT cells were stimulated with mLT-? At 10 ng / ml for 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min, and the amount of NF-? B was detected. (p: probe only. Only the labeled probe is added and the nuclear protein extract is not added)
Henan Toda Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.todafurniture.com